上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Amplite 荧光法汞离子定量试剂盒
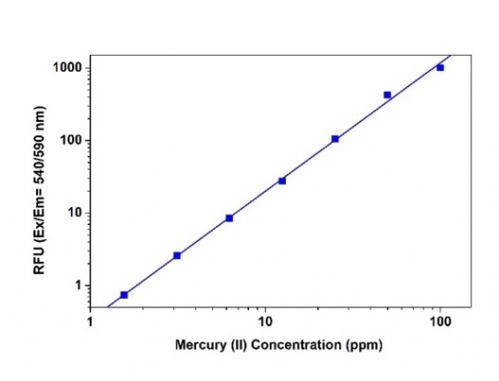 |
货号 | 19005 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 100 tests | 价格 | 3924 | |
| Ex (nm) | 540 | Em (nm) | 590 | |
| 分子量 | 溶剂 | |||
| 产品详细介绍 | ||||
简要概述
汞离子是一种必需的金属离子,在许多生物过程中起着重要作用。汞离子被认为是最危险的污染物和高危险物质之一。Hg2+的高毒性是由于它对蛋白质,DNA和酶等生物配体中的硫醇基团具有高亲和力。当Hg2+在人体内被环境吸收时,它会引起微管,离子通道和线粒体的畸变,可能会对肾脏,心脏,大脑,胃,肠,中枢神经系统和免疫系统造成严重损害。此外,汞在生态系统中通过食物链或大气积聚,并且由于其非生物降解而具有相对长的大气停留时间。由于各种原因,特别是其环境影响和生物并发症,已进行了深入研究。然而,很少有商业产品被开发用于快速检测汞离子。高选择性和灵敏的汞检测具有毒理学和环境重要性.Amplite 荧光汞离子定量试剂盒提供了一种强大的荧光测定方法,可高选择性地测量汞离子(Hg2+)。 Mercury Lite 590本身几乎不发荧光,但在结合Hg2+离子时会产生超过500倍的荧光增强。荧光信号可以用荧光酶标仪在Ex / Em = 540 / 590nm下测量。使用该试剂盒,我们能够在100μL反应体积中检测到低至8μMHg2+。
适用仪器
| 荧光酶标仪 | |
| 激发: | 540nm |
| 发射: | 590nm |
| cutoff: | 570nm |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色孔板 |
产品说明书
Hg2+检测样品分析方案
概述
1.准备汞工作溶液(50μL)
2.添加汞(II)标准品或测试样品(50μL)
3.在室温下孵育20-30分钟
4.在Ex / Em = 540/590 nm处监测荧光强度重要事项为了获得最佳效果,强烈建议使用黑色板。 在开始实验之前,在室温下解冻试剂盒组分
操作步骤
除非另有说明,否则所有未使用的储备溶液应分成一次性等分试样,并在制备后储存在-20°C。 避免反复冻融循环。
1.Mercury Lite 590原液(200X):
将25μLDMSO加入到Mercury Lite 590(组分A)的小瓶中并充分混合,避光。
注意单次使用等分试样,并将未使用的200X Mercury Lite 590原液储存在-20℃,避免光照和重复冻融循环。
2.汞(II)标准储备液(未提供):
我们使用高氯酸汞(II)水合物(Sigma 529656,CAS#304656-34-6)作为汞(II)标准。在ddH 2 O中制备浓度为1mM的汞(II)储备溶液。
3.汞(II)标准液配制
使用ddH2O进行1:2连续稀释,得到约500,250,125,62.5,
31.3,15.6和7.8μM连续稀释的汞(II)标准品(M7-M1)。
4.工作溶液配制
将25μLMercuryLite™590原液添加到5 mL分析缓冲液(组分B)中并充分混合(组分A + B)。
注意这种汞工作溶液足以容纳一个96孔板。 它不稳定,请及时使用。
5.实验步骤
5.1根据表1和2中提供的布局准备和添加汞(II)标准品(M),空白对照品(BL)和测试样品(TS)。对于384孔板,每个使用25μL试剂 而不是50μL。
5.2向每个汞(II)标准孔,空白对照和测试样品中加入50μL汞工作溶液,使总汞测定体积为100μL/孔。 对于384孔板,在每个孔中加入25μL汞工作溶液,总体积为50μL/孔。
5.3在室温下孵育反应20-30分钟,避光。
5.4用Ex / Em = 540 / 590nm,截止值570nm的荧光板读数器监测荧光增加。
参考文献
Coordination of mercury (II) to gold nanoparticle associated nitrotriazole towards sensitive colorimetric detection of mercuric ion with a tunable dynamic range
Authors: Chen, Xiaojun and Zu, Yanbing and Xie, Hong and Kemas, Aurino Muhammad and Gao, Zhiqiang
Journal: Analyst (2011): 1690–1696
Direct measurement of mercury (II) removal from organomercurial lyase (MerB) by tryptophan fluorescence: NmerA domain of coevolved γ-proteobacterial mercuric ion reductase (MerA) is more efficient than MerA catalytic core or glutathione
Authors: Hong, Baoyu and Nauss, Rachel and Harwood, Ian M and Miller, Susan M
Journal: Biochemistry (2010): 8187–8196
Sequence and analysis of a plasmid-encoded mercury resistance operon from Mycobacterium marinum identifies MerH, a new mercuric ion transporter
Authors: Schué, Mathieu and Dover, Lynn G and Besra, Gurdyal S and Parkhill, Julian and Brown, Nigel L
Journal: Journal of bacteriology (2009): 439–444
Is the cytoplasmic loop of MerT, the mercuric ion transport protein, involved in mercury transfer to the mercuric reductase?
Authors: Rossy, Emmanuel and Sénèque, Olivier and Lascoux, David and Lemaire, David and Crouzy, Serge and Delangle, Pascale and Covès, Jacques
Journal: FEBS letters (2004): 86–90
Mercuric ion attenuates nuclear factor-$kappa$B activation and DNA binding in normal rat kidney epithelial cells: implications for mercury-induced nephrotoxicity
Authors: Dieguez-Acuna, Francisco J and Ellis, Maureen E and Kushleika, John and Woods, James S
Journal: Toxicology and applied pharmacology (2001): 176–187
MerF is a mercury transport protein: different structures but a common mechanism for mercuric ion transporters?
Authors: Wilson, Jon R and Leang, Ching and Morby, Andrew P and Hobman, Jon L and Brown, Nigel L
Journal: FEBS letters (2000): 78–82
Overexpression of MerT, the mercuric ion transport protein of transposon Tn501, and genetic selection of mercury hypersensitivity mutations
Authors: Hobman, Jonathan L and Brown, Nigel L
Journal: Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1996): 129–134
Heat sensitivity of mercuric ion and organomercurial degrading enzymes of aquatic, mercury-resistant bacteria
Authors: Pahan, K and Ray, S and Gachhui, R and Chaudhuri, J and Mandal, A
Journal: World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (1993): 180–183
Uptake of metallic mercury and mercuric ion by human erythrocytes.
Authors: Ogata, M and Ishii, K and Meguro, T
Journal: Physiological chemistry and physics and medical NMR (1990): 135–140
Levels of metallic mercury and mercuric ion in the venous and arterial bloods of normal and acatalasemic mice following exposure to mercury vapor.
Authors: Aikoh, H and Ogata, M
Journal: Physiological chemistry and physics and medical NMR (1988): 177–181
相关产品
| 产品名称 | 货号 |
| Amplite 荧光法锌离子定量试剂盒 | Cat#19000 |
| Amplite 乙醇定量试剂盒 | Cat#40001 |
| Amplite 胆固醇定量试剂盒 | Cat#40006 |
